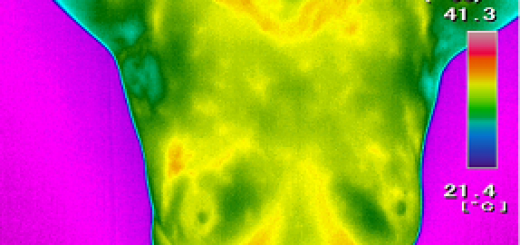
ترموگرافی درsctroal گاو
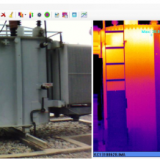
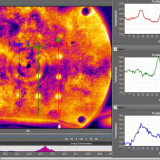
هدف از این مطالعه بررسی اثرات محیط بر روی کیفیت مایع منی در گاو، با استفاده از ترموگرافی مادون قرمز است.و به این نتیجه رسیدند که ترموگرافی مادون قرمز را می توان به ارزیابی درجه حرارت بیضه استفاده شود.
Abstract The aim of this study was to assess the seasonal effects of the environment on semen quality in bulls, using infrared thermography. Sperm motility (M), mass motion (MM), and vigor (VIG) were evaluated in sperm samples from 17 Bradford bulls aged approximately 24 months at the beginning of the study. Infrared thermography images and data were collected using an infrared FLIR T 300 camera and Quick Report 1.2 SP2 software to determine the temperature of the proximal and distal poles of the testis and to assess the testicular temperature gradient. The seasonal effects on physiological, seminal, and climatic variables were analyzed by the GLM ANOVA and CORR procedures using SAS®. The microclimatic factors were recorded in hourly intervals, and the daily mean temperature and mean relative humidity were calculated to determine the daily temperature-humidity index (THI) every day for 1 year. The temperature gradient (TG) variations of the testes were significantly higher in the autumn (4.5 °C), winter (4.0 °C), and spring (2.9 °C) compared to summer (0.9 °C) (P<0.05). Ocular globe temperatures were lower in the winter (27.6 °C) and autumn (26.8 °C) compared to summer (33.9 °C) and spring (31.1 °C) (P<0.05). The average MM (2.58), M (52.64), and VIG (2.70) of the semen decreased in the summer compared to other seasons (P<0.01). The TG was negatively correlated with THI (−0.44; P<0.05). For the seminal variables, MaD (−0.45; P<0.05) and TD (−0.50; P<0.01) presented a negative correlation with TG. The TG had a positive correlation between M and VIG, which had values of 0.36 and 0.35, respectively (P<0.05). We have concluded that infrared thermography can be used to assess the testicular temperature gradient and its consequences on physical and quantitative aspects of sperm.